400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
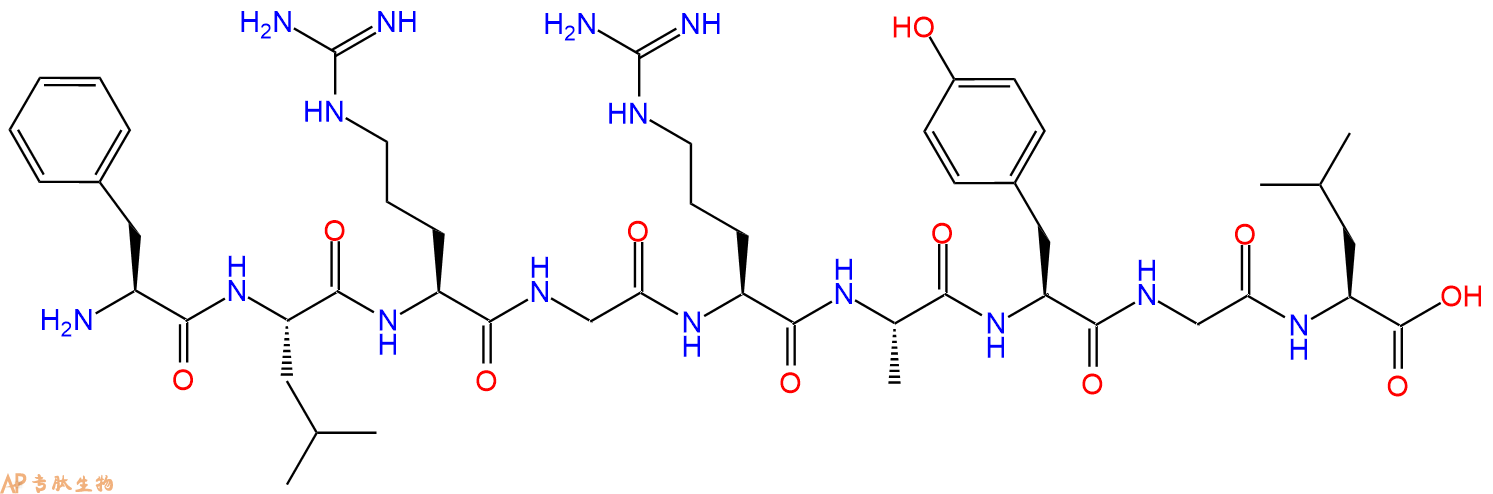
"Peptide H-FLRGRAYGL-OH is a Research Peptide with significant interest within the field academic and medical research. Recent citations using H-FLRGRAYGL-OH include the following: In Vitro Studies of MHC Class I Peptide Loading and Exchange M Bouvier - Antigen Processing: Methods and Protocols, 2019 - Springerhttps://link.springer.com/protocol/10.1007/978-1-4939-9450-2_6 T-cell receptor binding affects the dynamics of the peptide/MHC-I complex B Knapp , CM Deane - Journal of Chemical Information and ..., 2016 - ACS Publicationshttps://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00511 A structural basis for varied αβ TCR usage against an immunodominant EBV antigen restricted to a HLA-B8 molecule S Gras , PG Wilmann, Z Chen, H Halim- The Journal of ..., 2012 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/188/1/311/39100 Insights into the structure of the LC13 TCR/HLA-B8-EBV peptide complex with molecular dynamics simulations A Stavrakoudis - Cell biochemistry and biophysics, 2011 - Springerhttps://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12013-011-9151-2 A Structural Basis for Varied SRB Purcell, J McCluskey , J Halim, YC Liu- 2011 - academia.eduhttps://www.academia.edu/download/49937131/311.full.pdf Preferential binding of unusually long peptides to MHC class I and its influence on the selection of target peptides for T cell recognition JM Burrows, MJ Bell, R Brennan, JJ Miles - Molecular ..., 2008 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161589007007870 Amino acid 95 causes strong alteration of peptide position PΩ in HLA-B* 41 variants C Bade-Doeding, DS DeLuca , A Seltsam, R Blasczyk - Immunogenetics, 2007 - Springerhttps://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00251-007-0197-7 Analysis of interactions in a tapasin/class I complex provides a mechanism for peptide selection M Chen , M Bouvier - The EMBO journal, 2007 - embopress.orghttps://www.embopress.org/doi/abs/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601624 The structure of the human allo-\x90ligand HLA-\x90B* 3501 in complex with a cytochrome p450 peptide: Steric hindrance influences TCR allo-\x90recognition CS Hourigan , M Harkiolaki , NA Peterson- European journal of ..., 2006 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.200636234 Alloreactivity between disparate cognate and allogeneic pMHC-I complexes is the result of highly focused, peptide-dependent structural mimicry JK Archbold , WA Macdonald , JJ Miles - Journal of Biological ..., 2006 - ASBMBhttps://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(20)70616-2/fulltext Antagonism of antiviral and allogeneic activity of a human public CTL clonotype by a single altered peptide ligand: implications for allograft rejection LK Ely, KJ Green, T Beddoe , CS Clements- The Journal of ..., 2005 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/174/9/5593/72504 T cell receptor recognition of asuper-bulgedmajor histocompatibility complex class I-bound peptide FE Tynan, SR Burrows , AM Buckle , CS Clements- Nature ..., 2005 - nature.comhttps://www.nature.com/articles/ni1257 Novel strategy for identification of candidate cytotoxic T-\x90cell epitopes from human preproinsulin L Chang, L Kjer-\x90Nielsen, S Flynn, AG Brooks - Tissue ..., 2003 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00122.x Cutting edge: the minor histocompatibility antigen H60 peptide interacts with both H-2Kb and NKG2D A Cerwenka, CA OCallaghan- The Journal of ..., 2002 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/168/7/3131/34975 The structure of HLA-B8 complexed to an immunodominant viral determinant: peptide-induced conformational changes and a mode of MHC class I dimerization L Kjer-Nielsen, CS Clements, AG Brooks - The Journal of ..., 2002 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/169/9/5153/75164 The production, purification and crystallization of a soluble heterodimeric form of a highly selected T-cell receptor in its unliganded and liganded state CS Clements, L Kjer-Nielsen- Section D: Biological ..., 2002 - journals.iucr.orghttps://journals.iucr.org/d/issues/2002/12/00/cy0066/cy0066.pdf Peptide-MHC class I tetrameric complexes display exquisite ligand specificity SR Burrows , N Kienzle, A Winterhalter- The Journal of ..., 2000 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/165/11/6229/33743 The relationship between the cell surface density and the immunogenicity of multiple Epstein-Barr virus epitopes VL Crotzer - 2000 - search.proquest.comhttps://search.proquest.com/openview/06a0758b23e4b23671968815a6781078/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y Induction of Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses using dendritic cells pulsed with EBNA-3A peptides or UV-inactivated, recombinant EBNA M Subklewe, A Chahroudi - Blood, The Journal ..., 1999 - ashpublications.orghttps://ashpublications.org/blood/article-abstract/94/4/1372/249676 Differences in the recognition by CTL of peptides presented by the HLA-\x90B* 4402 and the HLA-\x90B* 4403 molecules which differ by a single amino acid J Herman, V Jongeneel , D Kuznetsov- Tissue ..., 1999 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1034/j.1399-0039.1999.530201.x The immunostimulatory effect of bio-active peptide from pollen on murine and human lymphocytes J Liu, S Wang, J Qi, X Wang, Y Song - Mechanisms of ageing and ..., 1998 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047637498000633 Human leukocyte antigen phenotype imposes complex constraints on the antigen-\x90specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte repertoire SR Burrows , SL Silins, SM Cross- European journal of ..., 1997 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830270126 -\x90Barr virus augment the alloresponse to common human leukocyte antigens: degenerate recognition of major histocompatibility complex-\x90bound peptide by T cells SR Burrows , SL Silins, R Khanna - European journal of ..., 1997 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830270720 T cell receptor repertoire for a viral epitope in humans is diversified by tolerance to a background major histocompatibility complex antigen. SR Burrows , SL Silins, DJ Moss, R Khanna - The Journal of ..., 1995 - rupress.orghttps://rupress.org/jem/article-abstract/182/6/1703/25482 Endoplasmic reticulum signal sequence facilitated transport of peptide epitopes restores immunogenicity of an antigen processing defective tumour cell line R Khanna , SR Burrows , V Argaet- International ..., 1994 - academic.oup.comhttps://academic.oup.com/intimm/article-abstract/6/4/639/714413 Peptide epitope induced apoptosis of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Implications for peripheral T cell deletion and peptide vaccination. A Suhrbier , SR Burrows , A Fernan- (Baltimore, Md.: 1950 ..., 1993 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article-abstract/150/6/2169/25848 The specificity of recognition of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope SR Burrows , SJ Rodda, A Suhrbier - European journal of ..., 1992 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830220128 Rapid visual assay of cytotoxic T-cell specificity utilizing synthetic peptide induced T-cell-T-cell killing. SR Burrows , A Suhrbier , R Khanna , DJ Moss - Immunology, 1992 - ncbi.nlm.nih.govhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1421752/ Inhibition of HLA B8-restricted recognition by unrelated peptides: evidence for allosteric inhibition A Fernan, SR Burrows , DJ Moss, A Saul , A Suhrbier - Immunology letters, 1991 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016524789190048F"
Definition
The CEF control peptides are 8-12 amino acids in length, with sequences derived from the human Cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr Virus and Influenza Virus1 These peptides are used in the stimulation of IFNg release from CD8+ T cells in individuals with defined HLA types1. They are useful as positive control peptides in several cytokine assays such as Elispot.
Discovery
CEF peptides were first selected in 2002 based on their ability to recognize CD8+ T cells1.
Classification
They are derived from epitopes of viruses and hence have antigenic properties1.
Structural Characteristics
CEF peptides are 8-11 amino acids long with sequences: GILGFVFTL (Influenza A, HLA-A2), FMYSDFHFI (Influenza A, HLA-A2), CLGGLLTMV (EBV, HLA-A2), GLCTLVAML (EBV, HLA-A2), NLVPMVATV (HCMV, HLA-A2).
Mode of action
CEF peptides are effective epitopes for CD8+ T cells2. They bind to these cells and trigger the production of IFNg.
Functions
CEF control peptides are used as positive control in Elispot assay that is used to investigate specific immune responses in various diseases including infections, cancer, allergies and autoimmune diseases2. In this case the CEF peptides ensure that the cells under study are active and viable2. Elispot is also useful in the development of vaccines especially for HIV where CEF peptides are used also as controls2.
References
1. Currier JR, Kuta EG, Turk E, Earhart LB, Loomis-Price L, Janetzki S, Ferrari G, Birx DL, Cox JH (2002). A panel of MHC class I restricted viral peptides for use as a quality control for vaccine trial ELISPOT assays, J Immunol Methods, 260, 157-172.
2. Gazagne A, Claret E, Wijdenes J, Yssel H, Bousquet F, Levy E, Vielh P, Scotte F, Goupil T, Fridman WH, Tartour E (2003). A Fluorospot assay to detect single T lymphocytes simultaneously producing multiple cytokines, J Immunol Methods, 283(1-2), 91-98.
Burrows, SR. et al. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 191 (1992).





