400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
这种肉豆蔻酰化的ARF-6是嗜铬细胞中钙诱发儿茶酚胺分泌和磷脂酶D激活的强抑制剂,非肉豆蔻酰化ARF-6和肉豆蔻酰化ASF-1的作用很小。
编号:434085
CAS号:
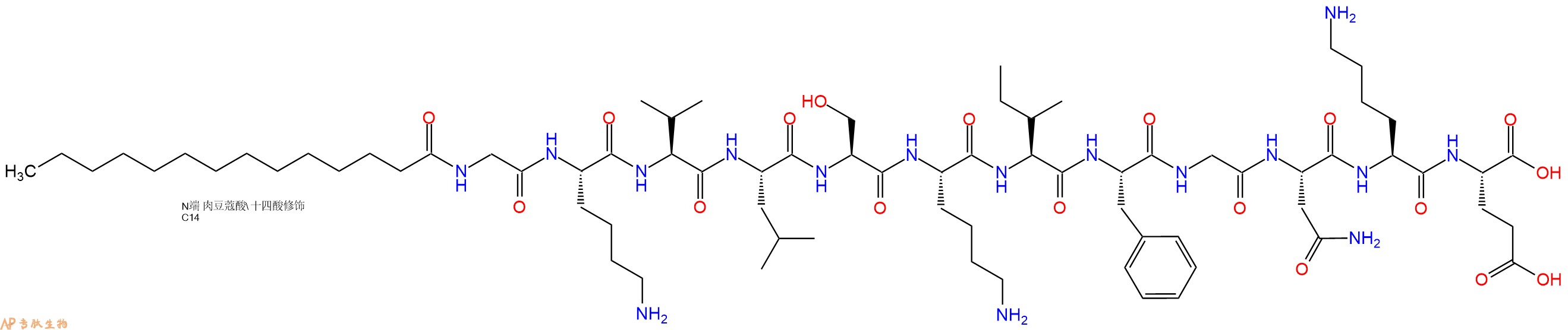
单字母:Myristicacid-GKVLSKIFGNKE-OH
ARF家族的成员在N-末端甘氨酸残基处进行肉豆蔻酰化,这是一种脂质共翻译修饰,似乎对功能活性至关重要。这种肉豆蔻酰化的ARF-6是嗜铬细胞中钙诱发儿茶酚胺分泌和磷脂酶D激活的强抑制剂,非肉豆蔻酰化ARF-6和肉豆蔻酰化ASF-1的作用很小。
Members of the ARF family are subjected to myristoylation at the N-terminal glycine residue, a lipid co-translational modification that appears essential for functional activity. This myristoylated ARF-6 is a strong inhibitor of calcium-evoked catecholamine secretion and phospholipase D activation in chromaffin cells, the non-myristoylated ARF-6 and the myristolated ARF-1 have mimimal effects.
这种肉豆蔻酰化的ARF-6是嗜铬细胞中钙诱发的儿茶酚胺分泌和磷脂酶D活化的强抑制剂。
This myristoylated ARF-6 is a strong inhibitor of calcium-evoked catecholamine secretion and phospholipase D activation in chromaffin cells.
肉豆蔻酰化ADP核糖基化因子6,myr-A用促进膜亲和力的N-肉豆蔻酰基模拟ARF6的N-末端区域。脂质锚有助于膜募集和曲率传感的研究。其序列保留了构象循环的关键切换残基。研究人员将其用于GTP酶机制分析和蛋白质-脂质相互作用测定。
Myristoylated ADP-Ribosylation Factor 6, myr-A models the N-terminal region of ARF6 with an N-myristoyl group that promotes membrane affinity. The lipid anchor facilitates studies of membrane recruitment and curvature sensing. Its sequence preserves key switching residues for conformational cycling. Researchers use it in GTPase mechanism analysis and protein-lipid interaction assays.
Definition
Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation factor (ARF) proteins are members of the GTP-binding proteins of the Ras superfamily1. They are major regulators of vesicle biogenesis in intracellular traffic, lipid metabolism, microtubule dynamics, development and other cellular processes2.
Discovery
ARF was originally identified as a cofactor for cholera toxin A catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory GTP-binding component of adenylate cyclase3.
Classification
The mammalian ARFs can be grouped into three classes on the basis of their size and sequence identity. ARF1, ARF2 and ARF3 are grouped under class I, ARF4 and ARF5 under class II and ARF6 under class III4.
Structural Characteristics
ARFs contain consensus amino acid sequences involved in GTP binding and hydrolysis which determine their catalytic activity3. They contain two switch regions, which change relative positions between cycles of GDP/GTP-binding. They are similar to heterotrimeric G protein subunits, these peptides are frequently myristoylated in their N-terminal region, which contributes to their membrane association.
Mode of action
The controlled binding and hydrolysis of GTP is critical to ARF function. ARF proteins cycle between GDP-bound, inactive and GTP-bound, active forms, and the cycling is regulated by specific guanine nucleotide releasing factors (GEPs) and GTPase-activating protein (GAPs). GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) hydrolyze bound GTP to GDP, and guanine nucleotide exchange factors adopt a new GTP molecule in place of a bound GDP. The GTP hydrolysis is required in many secretory pathways like formation and docking of vesicles at various membranes. It affects membrane traffic by recruiting coat proteins, including COPI and clathrin adaptor complexes to membranes.
Functions
ARFs function both constitutively within the secretory pathway and as targets of signal transduction in the cell periphery1. ARF proteins function in the regulation of membrane traffic and the organization of the cytoskeleton that are crucial to fundamental cellular processes, such as intracellular sorting/trafficking of newly synthesized proteins and endocytosis/exocytosis. They act at membrane surfaces to modify lipid composition and to recruit coat proteins for the generation of transport vesicles5. ARF proteins play a key regulatory role in the remodeling of actin cytoskeleton necessary for the formation of membrane ruffles and protrusions in association with phospholipase D and members of the Rho GTPase family. These activities of ARF proteins influence the formation, stability and functional integrity of epithelial junctions6.
References
1. Randazzo PA, Nie Z, Miura K, and Hsu VW, (2000). Molecular Aspects of the Cellular Activities of ADP-Ribosylation Factors. Sci. STKE, 2000 (59)
2. Pasqualato S, Renault L, Cherfils J (2002). Arf, Arl, Arp and Sar proteins: a family of GTP-binding proteins with a structural device for 'front-back' communication. EMBO Rep, 3(11):1035-41.
3. Kahn RA and Gilman AG (1984). Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J. Biol. Chem, 259, 6228-6234.
4. Donaldson JG (2008). Arfs and membrane lipids: sensing, generating and responding to membrane curvature. Biochem J, 414(2):189-94.
5. Moss J and Vaughan M (1995). Structure and Function of ARF Proteins: Activators of Cholera Toxin and Critical Components of Intracellular Vesicular Transport Processes. The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 270(21): 12327-12330.
6. Hiroi T (2009). Regulation of epithelial junctions by proteins of the ADP-ribosylation factor family. Front Biosci., 14:717-730.
烷基化肽-说明
专肽生物可提供多肽烷基化修饰,增加多肽一端的疏水性,例如常见的C18,C16,C14,C12,以及C6等,也可根据客户要求,接其他长度的烷基化链。
肉豆蔻酸修饰肽说明:
Myristyl group (Myristic acid), CH3(CH2)12–
肉豆蔻酸修饰肽的相关文献:
CPC Scientific serves as a supplier and partner to MYR Pharmaceuticals for developing bulevirtide (Hepcludex).
Nanoparticle delivery of immunostimulatory oligonucleotides enhances response to checkpoint inhibitor therapeutics
Buss, Colin G., and Sangeeta N. Bhatia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2020).
European Commission (EC) Grants Conditional Marketing Authorization (CMA) for MYR Pharmaceuticals HEPCLUDEX®.
A comparison of modular PEG incorporation strategies for stabilization of peptide-siRNA nanocomplexes.
Lo, Justin H., et al. Bioconjugate Chemistry (2016).
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-09-3563 | Arf6 plays an early role in platelet activation by collagen and convulxin | 下载 |





