400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
编号:429987
CAS号:77875-70-8
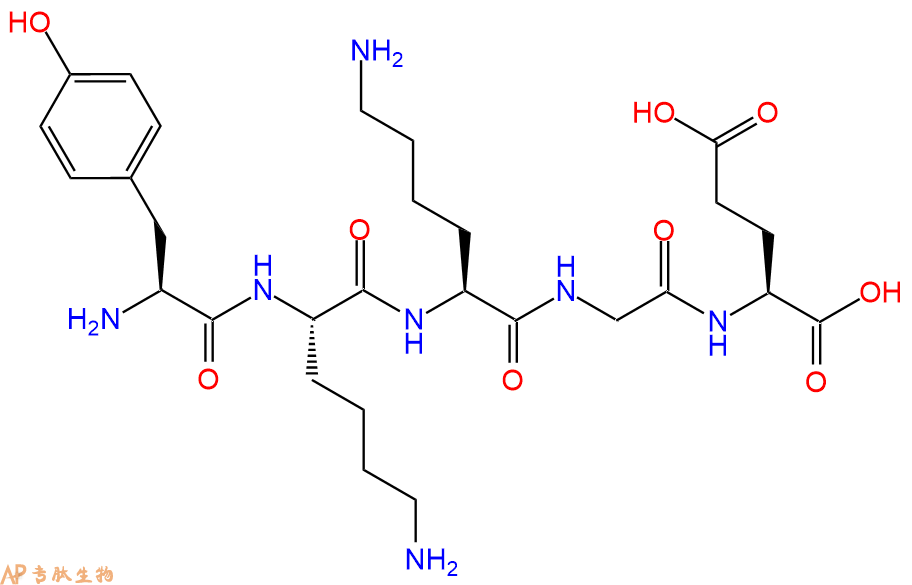
单字母:H2N-YKKGE-OH
| 编号: | 429987 |
| 中文名称: | 内啡肽β-Endorphin (27-31) (human)、促脂素β-Lipotropin (85-89) (human) |
| 英文名: | β-Endorphin (27-31) (human)、β-Lipotropin (85-89) (human) |
| CAS号: | 77875-70-8 |
| 单字母: | H2N-YKKGE-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基:N-terminal amino group。在肽或多肽链中含有游离a-氨基的氨基酸一端。在表示氨基酸序列时,通常将N端放在肽链的左边。 -TyrL-酪氨酸:tyrosine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-(4-羟基苯基)丙酸。是编码氨基酸。符号:Y,Tyr。 -LysL-赖氨酸:lysine。系统命名为(2S)-6-二氨基已酸。是编码氨基酸中的碱性氨基酸,哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。在蛋白质中的赖氨酸可以被修饰为多种形式的衍生物。符号:K,Lys。 -LysL-赖氨酸:lysine。系统命名为(2S)-6-二氨基已酸。是编码氨基酸中的碱性氨基酸,哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。在蛋白质中的赖氨酸可以被修饰为多种形式的衍生物。符号:K,Lys。 -Gly甘氨酸:glycine。系统命名为 2-氨基乙酸。是编码氨基酸中没有旋光性的最简单的氨基酸,因具有甜味而得名。符号:G,Gly。 -GluL-谷氨酸:glutamic acid。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-戊二酸。是编码氨基酸。符号:E,Glu。D-谷氨酸存在于多种细菌的细胞壁和某些细菌杆菌肽中。 -OHC端羧基:C-terminal carboxyl group。在肽或多肽链中含有游离羧基的氨基酸一端。在表示氨基酸序列时,通常将C端放在肽链的右边。 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 5 |
| 分子式: | C28H45N7O9 |
| 平均分子量: | 623.7 |
| 精确分子量: | 623.33 |
| 等电点(PI): | 10.92 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 2.98 |
| 平均亲水性: | 1.4 |
| 疏水性值: | -2.52 |
| 消光系数: | 1490 |
| 标签: | 未分类肽 |
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1210/endo-120-4-1472 | In vitro lipolytic activity of beta-endorphin and its partial sequences | 下载 |
| 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02914.x | Synthesis of human beta-endorphin in solution using benzyl-type side chain protective groups | 下载 |
| 10.1093/bja/aeg219 | Effects of endogenous and synthetic opioid peptides on neutrophil function in vitro | 下载 |





