400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
对 B10.A 小鼠鸽细胞色素c-启动的T细胞具有完全的刺激活性。对 Cytochrome c pigeon 反应的 I-Ek 限制性T细胞对 88-104 中具有特异性。
编号:182317
CAS号:86579-06-8
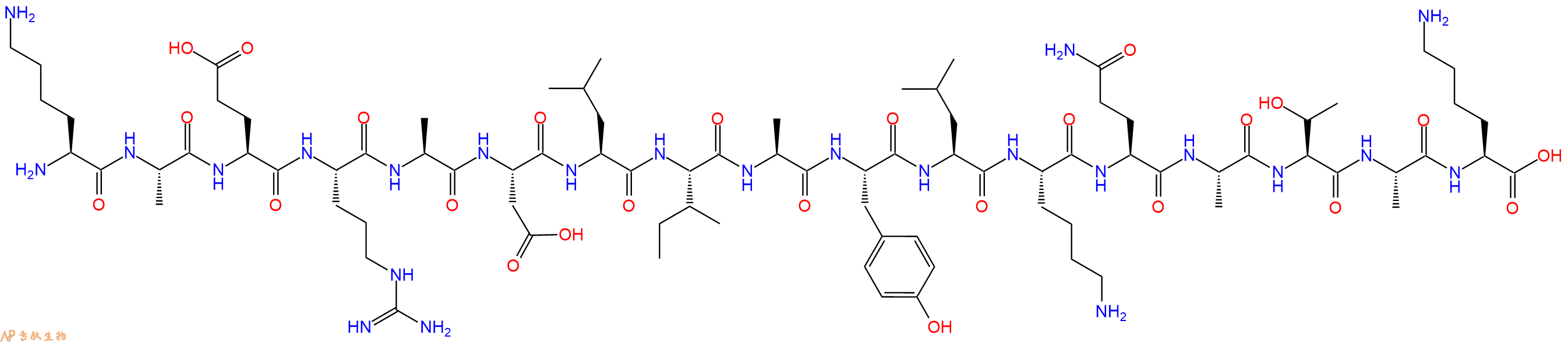
单字母:H2N-KAERADLIAYLKQATAK-OH
Cytochrome c-pigeon (88-104) (PCC 88-104) 对 B10.A 小鼠鸽细胞色素c-启动的T细胞具有完全的刺激活性。对 Cytochrome c pigeon 反应的 I-Ek 限制性T细胞对 88-104 中具有特异性。
Cytochrome c-pigeon (88-104) (PCC 88-104) has full stimulatory activity for pigeon cytochrome c-primed T cells from B10.A mice. The I-Ek-restricted T cell response to Cytochrome c pigeon (pcyt c) is specific for the COOH-terminal sequence 88-104.
氨基酸序列为H-Lys-Ala-Glu-Arg-Ala-Asp-Leu-Ile-Ala-Tyr-Leu-Lys-Gln-Ala-Thr-Ala-Lys-OH。
I-Ek-限制性T细胞对细胞色素C - 鸽子(pcyt c)COOH末端88-104多肽的应答是特异的。
T细胞激活所需的pcyt C多肽的最小长度为COOH末端序列含有的残基95-104。然而,残基95的NH2末端加入额外的残基可增加肽的抗原效力,最大效应是由pcyt c 88-104引起的。
取代细胞色素C多肽95到104之间的任何一个残基可以改变细胞色素C多肽对至少一种杂交瘤的抗原性。
用于研究T细胞反应的抗原序列。
An antigenic sequence used to study the T-cell response.
Kimachi K, et al. The minimal number of antigen-major histocompatibility complex class II complexes required for activation of naive and primed T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27(12):3310-3317. : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9464819/
Pincus MR, et al. Correlation between the conformation of cytochrome c peptides and their stimulatory activity in a T-lymphocyte proliferation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80(11):3297-3300. : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6304705/





