400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
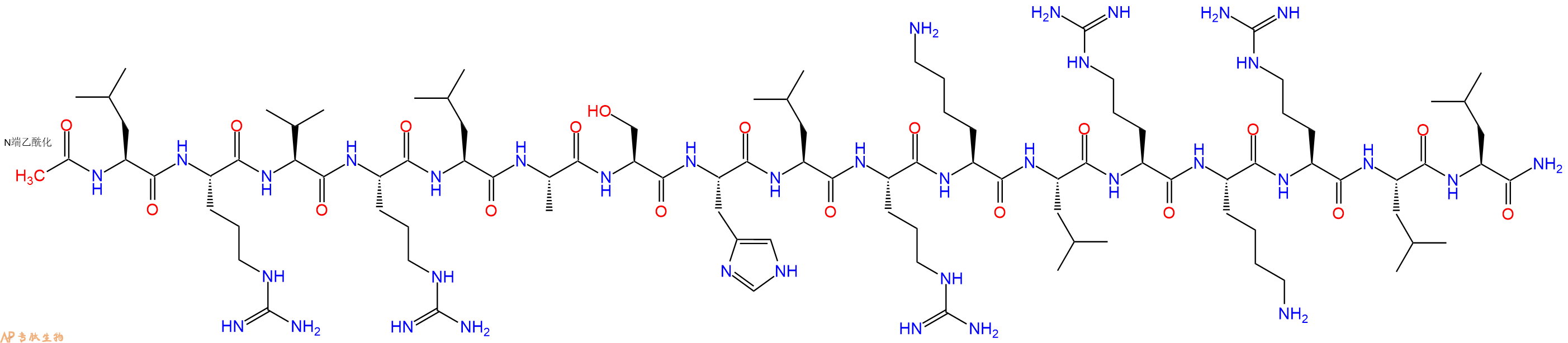
载脂蛋白 E (Apolipoprotein E, APOE) 肽的片段,与 ApoE 全息蛋白竞争结合 LDL 受体,具有有效的抗炎和神经保护作用。
编号:200724
CAS号:514200-66-9/2763583-75-9/2828432-37-5
单字母:Ac-LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL-CONH2
COG 133 TFA 是载脂蛋白 E (Apolipoprotein E, APOE) 肽的片段。COG 133 与 ApoE 全息蛋白竞争结合 LDL 受体,具有有效的抗炎和神经保护作用。COG 133 TFA 也是 nAChR 拮抗剂,IC50 为 445 nM。
COG 133 TFA is a fragment of Apolipoprotein E (APOE) peptide. COG 133 TFA competes with the ApoE holoprotein for binding the LDL receptor, with potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. COG 133 TFA is also a nAChR antagonist with an IC50 of 445 nM[1][2].
COG133是载脂蛋白E(APOE)肽的片段,具有强大的抗炎和神经保护作用。COG 133也是nAChR拮抗剂,其IC50为445nM。COG133(0.02、0.2和2.0μM)改善了无谷氨酰胺培养基中的细胞数量。在IEC-6细胞中,COG133(0.2-20μM)改善了5-FU激发后的细胞迁移,达到了与对照组相同的迁移水平。COG133(3μM)显著增加C57BL6J野生型动物的有丝分裂隐窝数量。COG133治疗改善了隐窝结构并减少了固有层炎症。COG133(3μM)可显著降低肠道MPO水平。COG133部分降低5-FU处理小鼠近端小肠的TNF-α水平。在野生型和ApoE敲除小鼠中,COG 133(3μM)逆转了5-FU诱导的近端肠中Tunel阳性细胞的增加。COG133在改善的肠粘膜中引起NF-κB的高表达。
COG 133 is a fragment of Apolipoprotein E (APOE) peptide with potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. COG 133 is also a nAChR antagonist with an IC50 of 445 nM. COG 133 (0.02, 0.2, and 2.0 μM) improved cell numbers in glutamine free media. In IEC-6 cells, COG 133 (0.2-20 μM) improved cell migration following 5-FU challenge, reaching the same migration level as controls. COG 133 (3 μM) significantly increased the mitotic crypt numbers in C57BL6J wild-type animals. COG 133 treatment improved crypt architecture and reduced lamina propria inflammation. COG 133 (3 μM) significantly reduced the intestinal MPO levels. COG 133 partially decreased TNF-α level in the proximal small intestine from 5-FU-treated mice. In both wild-type and ApoE knock-out mice, COG 133 (3 μM) reverted the increase in Tunel-positive cells in the proximal intestine induced by 5-FU. COG 133 caused higher expression of the NF-κB in the improved intestinal mucosa.
COG 133的化学式为C97H181N37O19,氨基酸序列为Ac-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Leu-Ala-Ser-His-Leu-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-Lys-Arg-Leu-Leu-amide,分子量为2169.73。载脂蛋白E(ApoE)含有299个氨基酸,它参与运输脂蛋白、脂溶性维生素和胆固醇进入淋巴系统,然后进入血液。它主要在肝脏中合成,但在其它组织如脑、肾和脾也有发现。载脂蛋白E主要产生于神经系统、非神经元细胞以及星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞,神经元优先表达APOE的受体。目前鉴定得到了哺乳动物的七种APOE受体,APOE受体属于低密度脂蛋白受体家族,进化上相对保守。最初发现APOE是因其在脂蛋白代谢和心血管疾病中的重要性。APOE缺陷导致家族性血β脂蛋白异常,又称Ⅲ型高脂蛋白血症(HLP III),其中乳糜微粒、极低密度脂蛋白和低密度脂蛋白的残余物清除受损,造成血浆胆固醇和甘油三酯增加。最近研究了其在与脂蛋白运输没有直接关系的生物学过程中的作用,包括阿尔兹海默症(AD)、免疫调节和认知。
COG 133 acetate is a fragment of ApoE that exhibits anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects and could also be an antagonist at α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
COG 133醋酸盐是ApoE的一个片段,具有抗炎和神经保护作用,也可能是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的拮抗剂。
COG133 is a peptide fragment of ApoE that corresponds to residues 133-149 of the ApoE LDL receptor-binding domain and an antagonist of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs; IC50 = 720 nM). It suppresses TNF-α and nitric oxide (NO) release in BV-2 microglia when used at concentrations ranging from 10 to 50 µM.
COG133是ApoE的肽片段,其对应于ApoE LDL受体结合结构域的残基133-149,并且是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体(nAChRs;IC50=720nM)的拮抗剂。当浓度为10至50µM时,它可以抑制BV-2小胶质细胞中TNF-α和一氧化氮(NO)的释放。
Apolipoprotein E fragment (133-149) – COG133: acetyl-LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL-NH2 (CAS : 514200-66-9)\n\nSB-PEPTIDE offers Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) mimetic peptide COG133 – LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL – which competes with the ApoE holoprotein for binding the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor.\n\nApolipoprotein E (ApoE): A key player in lipid transport and beyond\n\nApolipoprotein E (apoE) is a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor ligand that belongs to the family of fat-binding proteins, known as apolipoproteins. While the liver and macrophages primarily produce ApoE in peripheral tissues to mediate cholesterol metabolism, in the central nervous system (CNS), astrocytes take the lead in producing ApoE.\n\nApoE plays a vital role in lipid transport, facilitating the movement of lipids such as fats, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins between organs via plasma and interstitial fluids. In the central CNS, it serves as a crucial cholesterol carrier, promoting neuron survival, sprouting, and exhibiting functional anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.\nBeyond its role in lipid transport, ApoE binds to a diverse range of cellular receptors, influencing immune responses, promoting cell migration, and potentially impacting transcription regulation.\nWith its multifaceted functions, ApoE stands as a cornerstone in maintaining plasma and tissue lipid homeostasis and orchestrating complex interplays within the body.\n\nApoE(133-149) mimetic peptide : COG 133\n\nCOG 133 mimetic peptide, takes the incredible capabilities of acting the same way as the LDL receptor-binding domain of ApoE. Therefore, this peptide wields a non-competitive stance against the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, which is not only implicated in long-term memory but also in neurotoxicity, stroke, myocardial infarction, sepsis, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer progression, and angiogenic/neurogenic activity. Moreover, COG133’s anti-apoptotic effects further accentuate its potential.\nBy mimicking ApoE, COG 133 / ApoE(133-149) masterfully inhibits the NMDA receptor channel function through interactions with the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. The peptide emerged as a potent agent in reducing inflammation, cellular infiltration, and demyelination, making strides in animal models of multiple sclerosis (MS) and the 5-fluorouracil model of intestinal mucositis.\nIndeed, COG-133 emerged as a champion to suppress symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), curbing inflammation, demyelination, and cell infiltration in the spinal cord. ApoE (133-149) fragment additionally showcased its prowess by decreasing TNF-α and nitric oxide (NO) release in BV-2 microglia and counteracting LPS-induced increases in brain levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in mice. The peptide also stands as a guardian of hippocampal neuronal health and offers promise in delaying disease onset and reducing severity of EAE mouse model.\n\nCOG-133 applications\n\nThe applications of COG 133 (ApoE 133-149) resonate across diverse fields of research and healthcare.\nGenerally speaking, COG133’s multifaceted influences on inflammation, cellular responses, and neuronal health open doors to novel therapies for neurological disorders.\nIts potential as a groundbreaking tool in understanding and combating MS holds the promise of improved treatments and enhanced quality of life for patients suffering from this particular disease.\nSB-PEPTIDE is proud to offer this remarkable peptide for neurological research!
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1186/1471-230X-12-35 | Apolipoprotein E COG 133 mimetic peptide improves 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis | 下载 |
| 10.1124/jpet.105.095505 | Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides block alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in xenopus oocytes | 下载 |
| 10.1172/jci.insight.134539 | Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophage apolipoprotein E participates in pulmonary fibrosis resolution | 下载 |
多肽Ac-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Leu-Ala-Ser-His-Leu-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-Lys-Arg-Leu-Leu-NH2的合成步骤:
1、合成MBHA树脂:取若干克MBHA树脂(如初始取代度为0.5mmol/g)和1倍树脂摩尔量的Fmoc-Linker-OH加入到反应器中,加入DMF,搅拌使氨基酸完全溶解。再加入树脂2倍量的DIEPA,搅拌混合均匀。再加入树脂0.95倍量的HBTU,搅拌混合均匀。反应3-4小时后,用DMF洗涤3次。用2倍树脂体积的10%乙酸酐/DMF 进行封端30分钟。然后再用DMF洗涤3次,甲醇洗涤2次,DCM洗涤2次,再用甲醇洗涤2次。真空干燥12小时以上,得到干燥的树脂{Fmoc-Linker-MHBA Resin},测定取代度。这里测得取代度为 0.3mmol/g。结构如下图:
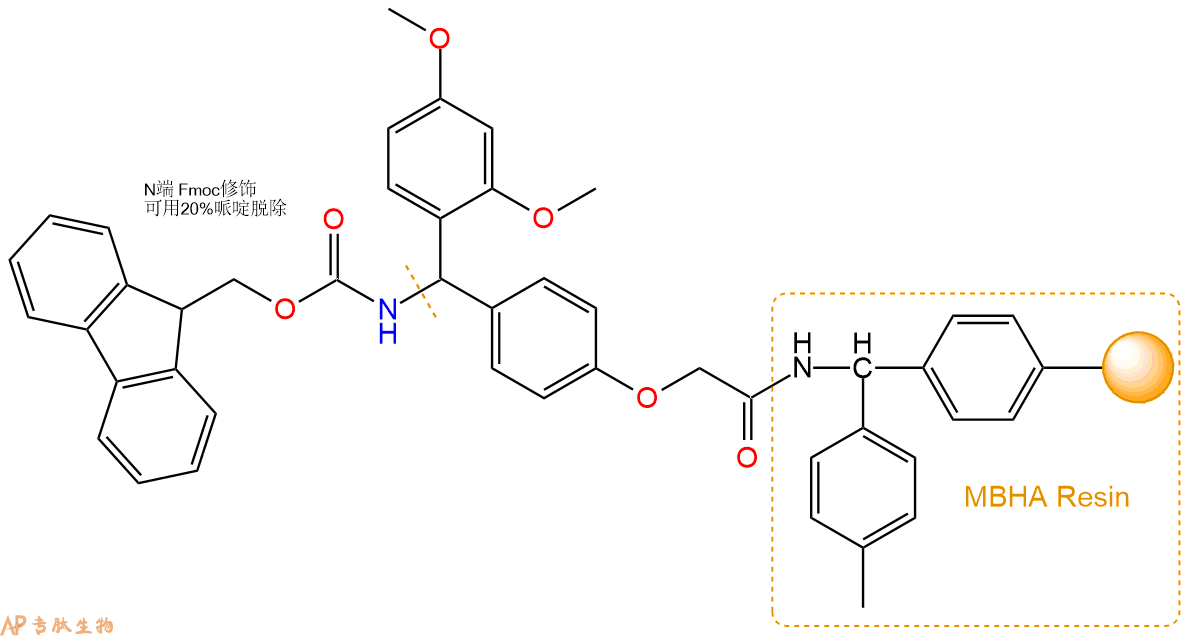
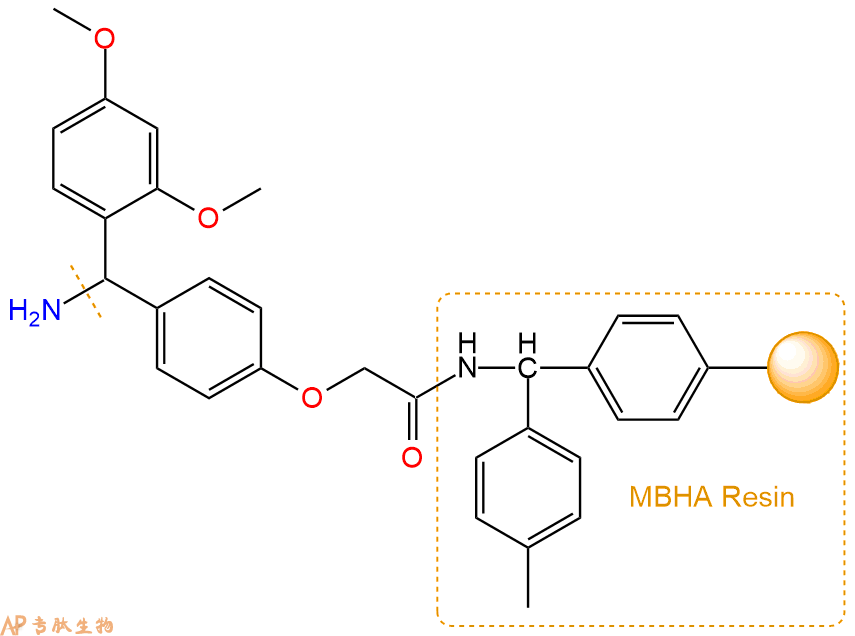
2、脱Fmoc:取2.62g的上述树脂,用DCM或DMF溶胀20分钟。用DMF洗涤2遍。加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Linker-MBHA Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
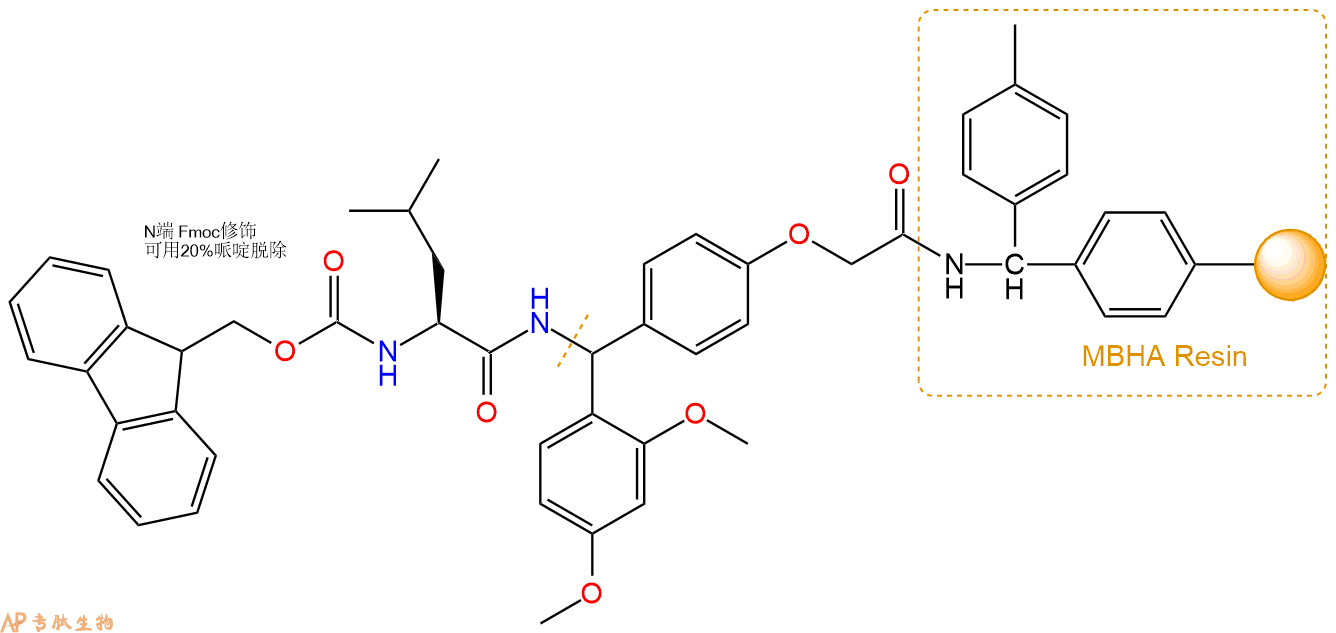
3、缩合:取2.36mmol Fmoc-Leu-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入4.72mmol DIPEA,2.24mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHA Resin,结构如下:
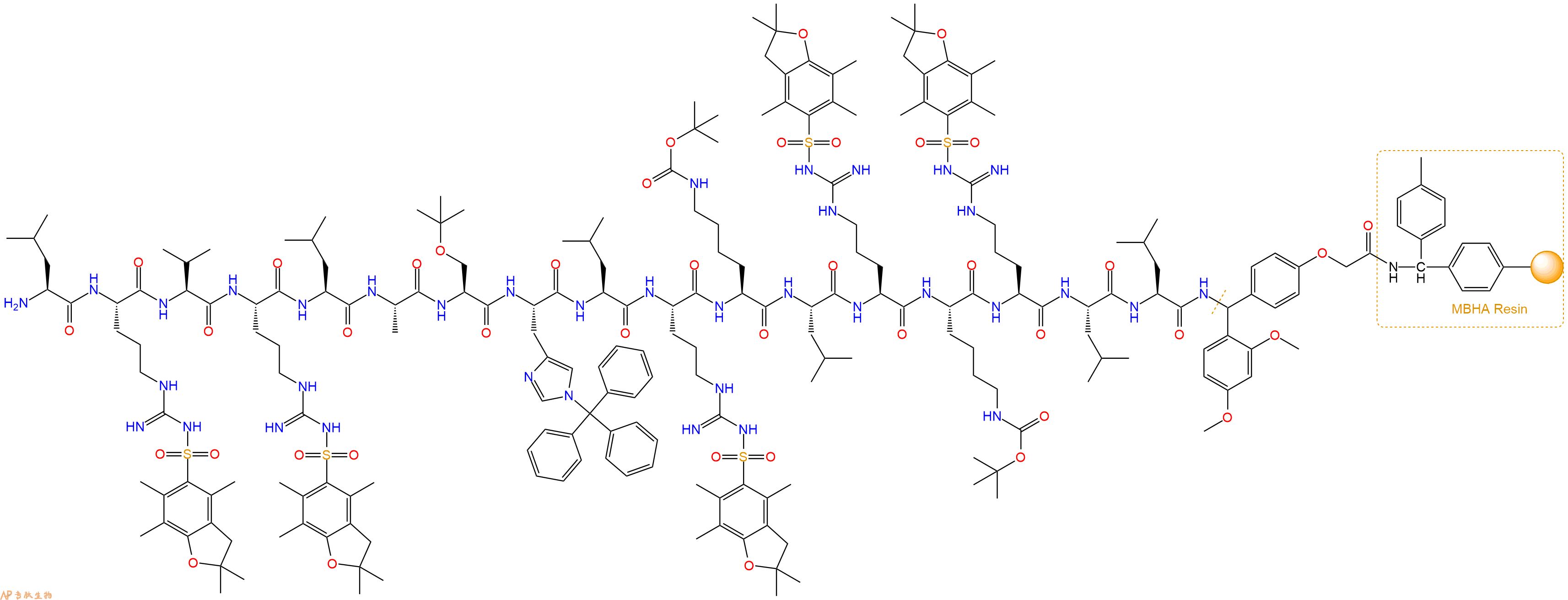
5、乙酸酐反应连接:在上述树脂中,加入适当DMF后,再加入2.36mmol乙酸酐到树脂中,再加入4.72mmol DIPEA,鼓氮气反应30分钟。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。 得到Ac-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Val-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Ala-Ser(tBu)-His(Trt)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Leu-Arg(Pbf)-Lys(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Leu-Leu-Linker-MBHAResin。 结构如下:
6、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品Ac-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Leu-Ala-Ser-His-Leu-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-Lys-Arg-Leu-Leu-NH2。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
7、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
8、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。





