400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
这种ARF-6片段和肉豆蔻酰化ARF-1对嗜铬细胞中钙诱发的儿茶酚胺分泌和磷脂酶D活化的抑制作用很小,而肉豆蔻酰化的ARF6具有强烈的抑制作用。
编号:147074
CAS号:
单字母:H2N-GKVLSKIFGNKE-OH
这种ARF-6片段和肉豆蔻酰化ARF-1对嗜铬细胞中钙诱发的儿茶酚胺分泌和磷脂酶D活化的抑制作用很小,而肉豆蔻酰化的ARF6具有强烈的抑制作用。
This ARF-6 fragment and the myristoylated ARF-1 have minimal inhibitory effects on calcium-evoked catecholamine secretion and phospholipase D activation in chromaffin cells, in contrast to the strongly inhibitory effect of myristoylated ARF6.
ADP核糖基化因子(ARF)和类ARF蛋白是一类高度保守的Ras相关GTP酶家族。
ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) and ARF-like proteins are a family of highly conserved Ras-related GTPases.
ADP核糖基化因子6,ARF6(2-13)是一个N端片段,对于探索膜结合基序和构象转换非常重要。其两亲性残基支持脂质相互作用和结构转变的研究。该肽有助于绘制ARF蛋白的调控表面。应用包括分子信号和蛋白质折叠分析。
ADP-Ribosylation Factor 6, ARF6 (2-13) is an N-terminal segment important for exploring membrane-association motifs and conformational switching. Its amphipathic residues support studies of lipid interaction and structural transitions. The peptide aids in mapping regulatory surfaces of ARF proteins. Applications include molecular signaling and protein-folding analysis.
Definition
Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation factor (ARF) proteins are members of the GTP-binding proteins of the Ras superfamily1. They are major regulators of vesicle biogenesis in intracellular traffic, lipid metabolism, microtubule dynamics, development and other cellular processes2.
Discovery
ARF was originally identified as a cofactor for cholera toxin A catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory GTP-binding component of adenylate cyclase3.
Classification
The mammalian ARFs can be grouped into three classes on the basis of their size and sequence identity. ARF1, ARF2 and ARF3 are grouped under class I, ARF4 and ARF5 under class II and ARF6 under class III4.
Structural Characteristics
ARFs contain consensus amino acid sequences involved in GTP binding and hydrolysis which determine their catalytic activity3. They contain two switch regions, which change relative positions between cycles of GDP/GTP-binding. They are similar to heterotrimeric G protein subunits, these peptides are frequently myristoylated in their N-terminal region, which contributes to their membrane association.
Mode of action
The controlled binding and hydrolysis of GTP is critical to ARF function. ARF proteins cycle between GDP-bound, inactive and GTP-bound, active forms, and the cycling is regulated by specific guanine nucleotide releasing factors (GEPs) and GTPase-activating protein (GAPs). GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) hydrolyze bound GTP to GDP, and guanine nucleotide exchange factors adopt a new GTP molecule in place of a bound GDP. The GTP hydrolysis is required in many secretory pathways like formation and docking of vesicles at various membranes. It affects membrane traffic by recruiting coat proteins, including COPI and clathrin adaptor complexes to membranes.
Functions
ARFs function both constitutively within the secretory pathway and as targets of signal transduction in the cell periphery1. ARF proteins function in the regulation of membrane traffic and the organization of the cytoskeleton that are crucial to fundamental cellular processes, such as intracellular sorting/trafficking of newly synthesized proteins and endocytosis/exocytosis. They act at membrane surfaces to modify lipid composition and to recruit coat proteins for the generation of transport vesicles5. ARF proteins play a key regulatory role in the remodeling of actin cytoskeleton necessary for the formation of membrane ruffles and protrusions in association with phospholipase D and members of the Rho GTPase family. These activities of ARF proteins influence the formation, stability and functional integrity of epithelial junctions6.
References
1. Randazzo PA, Nie Z, Miura K, and Hsu VW, (2000). Molecular Aspects of the Cellular Activities of ADP-Ribosylation Factors. Sci. STKE, 2000 (59)
2. Pasqualato S, Renault L, Cherfils J (2002). Arf, Arl, Arp and Sar proteins: a family of GTP-binding proteins with a structural device for 'front-back' communication. EMBO Rep, 3(11):1035-41.
3. Kahn RA and Gilman AG (1984). Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J. Biol. Chem, 259, 6228-6234.
4. Donaldson JG (2008). Arfs and membrane lipids: sensing, generating and responding to membrane curvature. Biochem J, 414(2):189-94.
5. Moss J and Vaughan M (1995). Structure and Function of ARF Proteins: Activators of Cholera Toxin and Critical Components of Intracellular Vesicular Transport Processes. The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 270(21): 12327-12330.
6. Hiroi T (2009). Regulation of epithelial junctions by proteins of the ADP-ribosylation factor family. Front Biosci., 14:717-730.
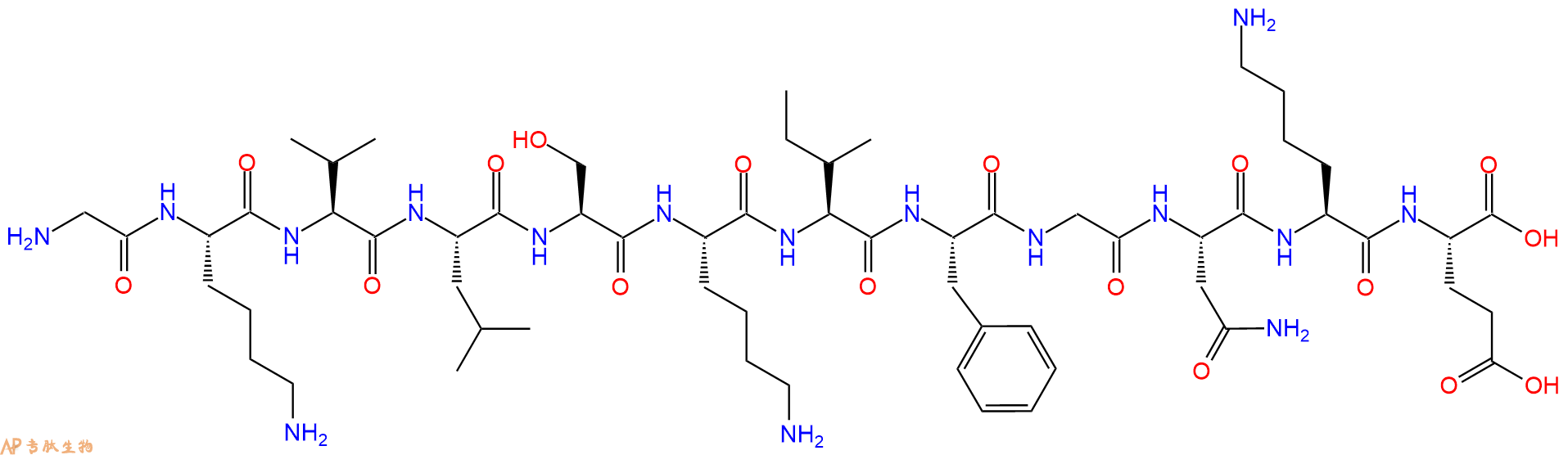
多肽H2N-Gly-Lys-Val-Leu-Ser-Lys-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn-Lys-Glu-COOH的合成步骤:
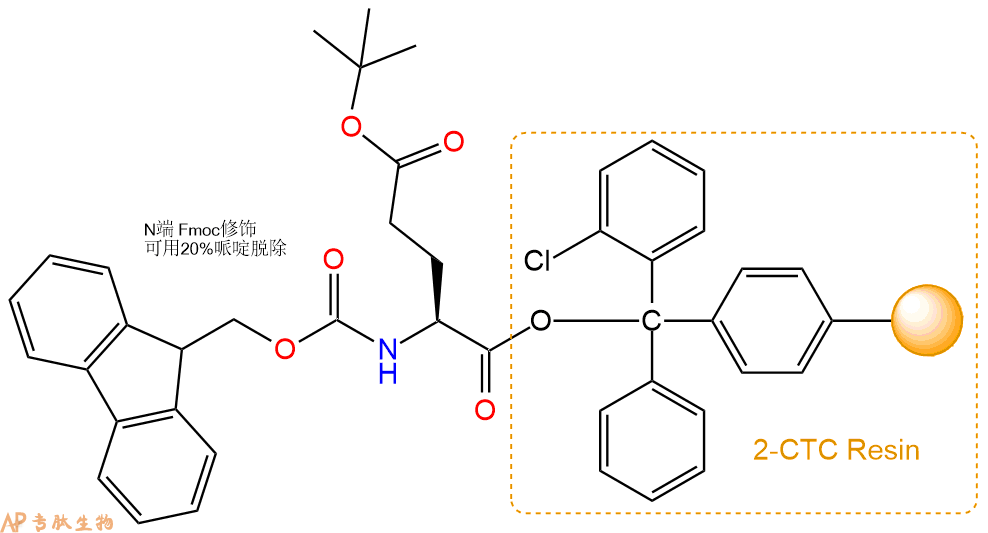
1、合成CTC树脂:称取1.48g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为1.04mmol/g)和1.85mmol Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入4.62mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
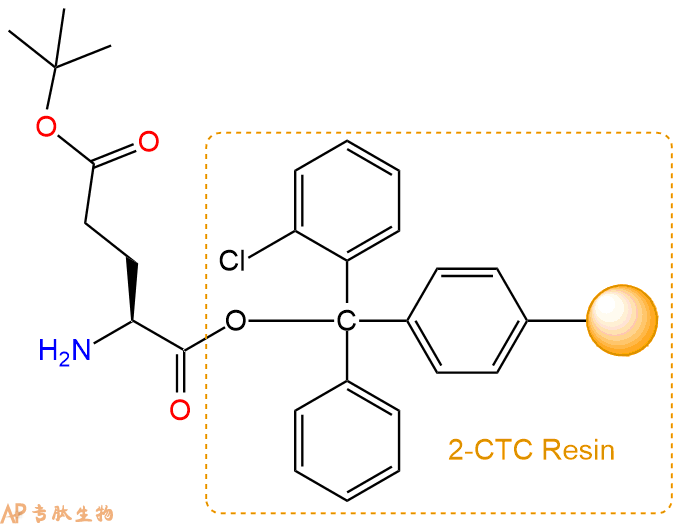
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
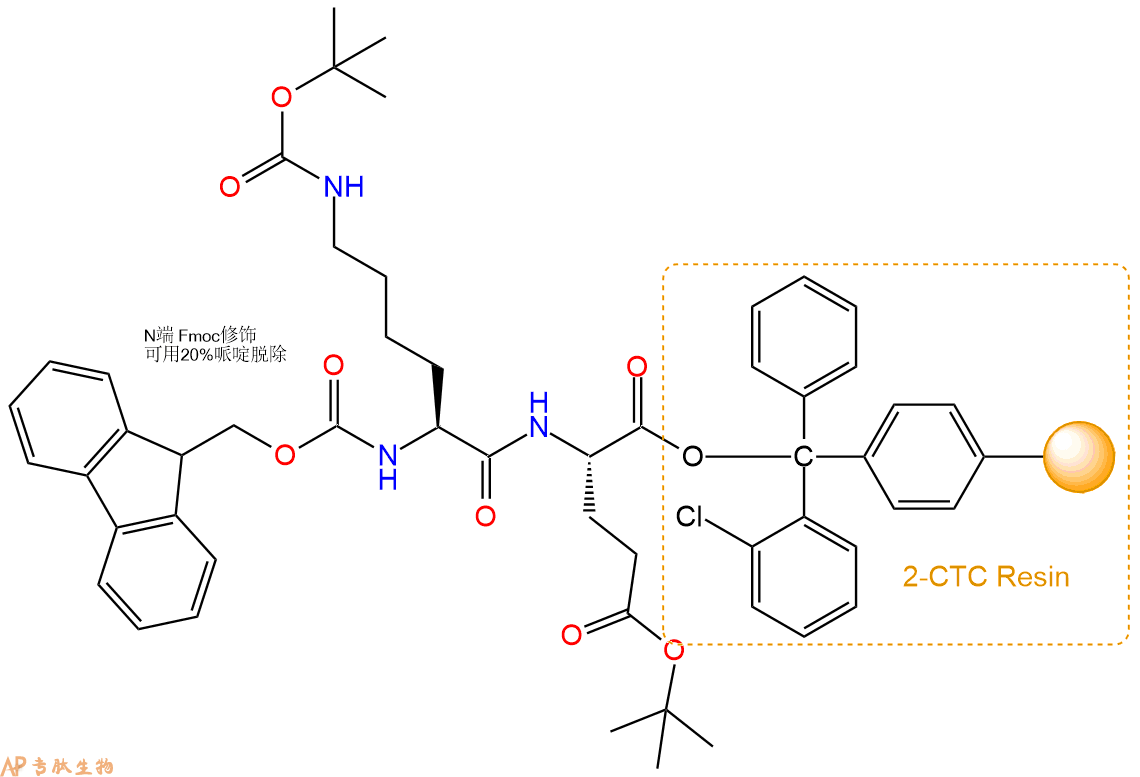
3、缩合:取4.62mmol Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入9.24mmol DIPEA,4.39mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Lys(Boc)-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Gly-Lys(Boc)-Val-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn(Trt)-Lys(Boc)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin,结构如下:
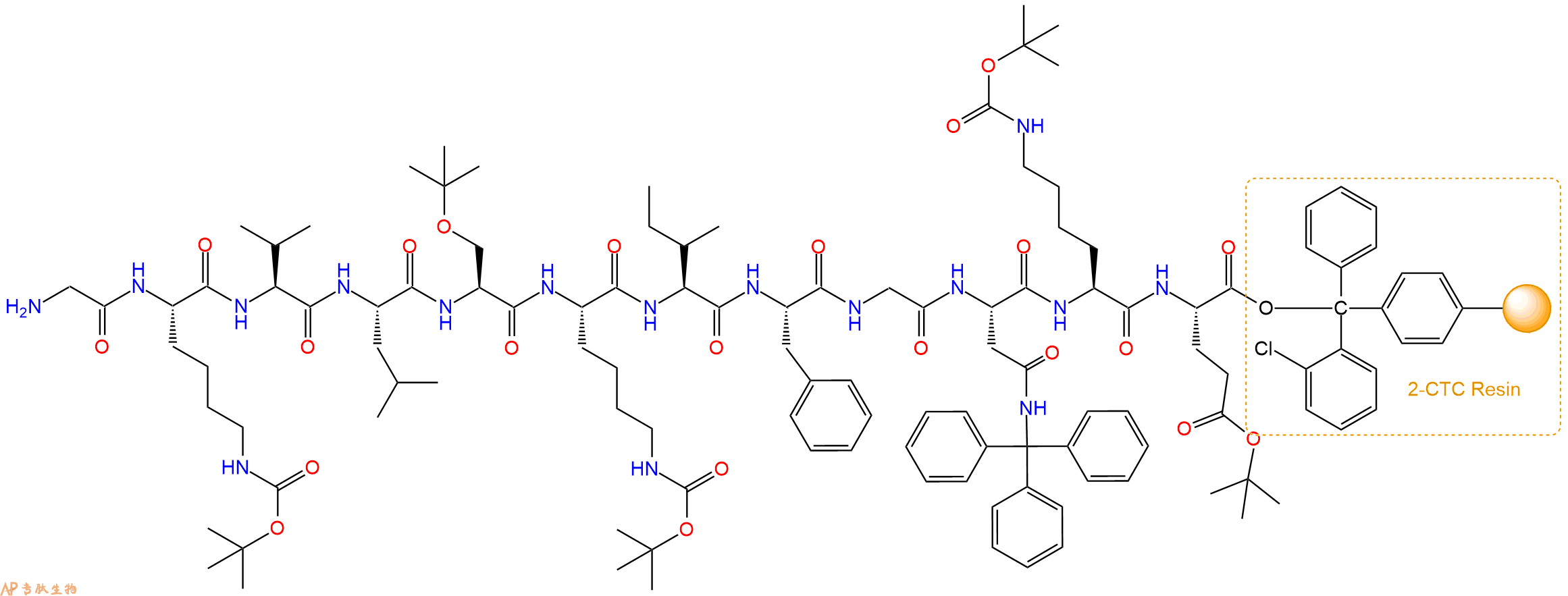
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Gly-Lys-Val-Leu-Ser-Lys-Ile-Phe-Gly-Asn-Lys-Glu-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。





