400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
由激肽释放酶-激肽系统产生的活性肽。 它是炎症调节因子,也被认为是几种血管和肾功能以及神经调节因子。
编号:122160
CAS号:58-82-2/227-781-2/6846-03-3
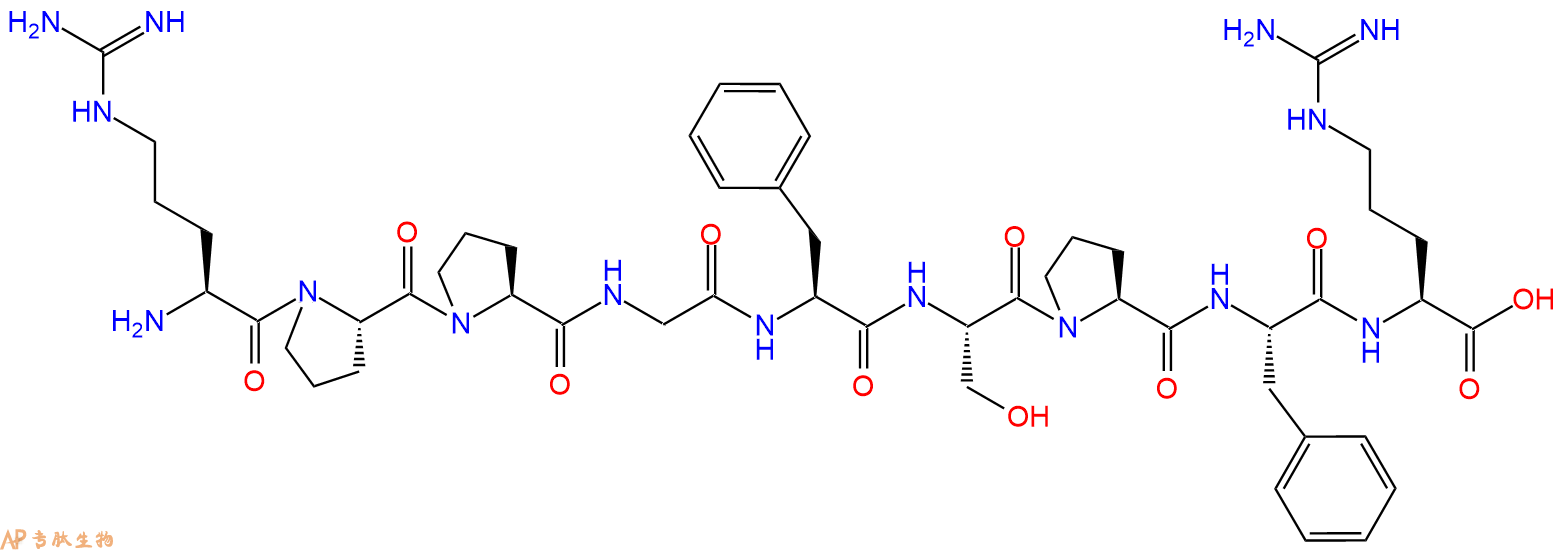
单字母:H2N-RPPGFSPFR-OH
Bradykinin是由激肽释放酶-激肽系统产生的活性肽。 它是炎症调节因子,也被认为是几种血管和肾功能以及神经调节因子。
Bradykinin is an active peptide that is generated by the kallikrein-kinin system. It is a inflammatory mediator and also recognized as a neuromediator and regulator of several vascular and renal functions.
该肽是血管紧张素I转换酶(ACE I)的抑制剂,来源于缓激肽。ACE I部分抑制肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS),该系统调节血压并可能介导高血压。ACE I利用锌和氯依赖性机制将血管紧张素I转化为具有生物活性的肽血管紧张素II。
This peptide is an inhibitor for Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE I), derived from Bradykinin. ACE I partially suppresses the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and may mediate hypertension. ACE I converts angiotensin I to the biologically active peptide angiotensin II using a zinc- and chloride- dependent mechanism.
Bradykinin 是一种有效的内皮依赖性血管扩张剂,可降低血压。Bradykinin 可引起支气管和肠道非血管平滑肌的收缩,增加血管通透性,并参与疼痛的机制。
Bradykinin is an effective endothelium-dependent vasodilator that can lower blood pressure. Bradykinin can induce contraction of bronchial and intestinal non-vascular smooth muscle, increase vascular permeability, and participate in the mechanism of pain.
缓激肽是一种由体内激酶产生的肽类激素。它是离子通道的激活剂,也是G蛋白偶联受体B1、B2和B3的配体。缓激肽被用作研究细胞生物学、药理学和生命科学的研究工具。它与红细胞蛋白带4.4、α-2-巨球蛋白受体、α-银环蛇毒素结合蛋白、β-链整合素受体和血小板膜糖蛋白IIb/IIIa受体等蛋白质相互作用。研究表明,缓激肽可抑制缓激肽B1受体(Ki=0.4 nM)和缓激肽B2受体(Ki=0.6 nM)的活性。
Bradykinin is a peptide hormone that is produced in the body by the kininase enzyme. It is an activator of ion channels and ligand for the G-protein coupled receptors B1, B2, and B3. Bradykinin is used as a research tool to study cell biology, pharmacology, and life science. It interacts with proteins such as erythrocyte protein band 4.4, alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor, alpha-bungarotoxin binding protein, beta-chain integrin receptor, and platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor. Bradykinin has been shown to inhibit the activity of bradykinin B1 receptor (Ki = 0.4 nM) and bradykinin B2 receptor (Ki = 0.6 nM).
缓激肽能收缩平滑肌、舒张血管并增加血管通透性。其其他生理功能还包括刺激疼痛感受器、抑制环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)的积累以及诱导一氧化氮的释放。
Bradykinin that contracts smooth muscles, relaxes blood vessels and increases vascular permeability. Additional physiological functions include the stimulation of pain receptors, inhibition of cAMP accumulation, and induction of the release of nitric oxide.
Definition
Bradykinin is a nonapeptide that is mainly found in animal preparations that are treated with the venom of the snake, Bothrops jararaca1,2. It dialates blood vessels that in turn leads to decrease in blood pressure2. Bradykinin analogs are slightly modified structural derivatives of bradykinin that perform similar functions as bradykinin3.
Discovery
Bradykinin was discovered in the blood plasma of animals that were treated with the venom from the Brazilian snake, Bothrops jararaca1,2. The discovery was part of a study that was related to toxicology of snake bites. Bradykinin analogs were synthesized by solid-phase techniques in 1975 and their function was studied in rats and rabbits3.
Classification
Bradykinin is a 9 amino acid peptide that belongs to the kinin family of proteins4. It has homologs in several animals including other snakes, frog, dog and humans4.
Structural Characteristics
Bradykinin has the sequence Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg3. Several analogs of bradykinin have been synthesized. They are also nanopeptides containing substitutions of various amino acids of bradykinin. For example two analogs of bradykinin were synthesized one with 7-beta-homo-L-proline and the other with 8-beta-homo-L-phenylalanine substitutions3. It was found that both of them are resistant to enzymatic degradation3.
Mode of action
Bradykinin binds to two different kinin G protein coupled receptors- B1 and B25. Upon binding to these receptors it induces conversion of GTP to GDP which in turn triggers the conversion ATP to cAM which then acts as a second messenger resulting in the activation of genes. B1 receptor is expressed as a result of tissue injury and is found to play a role in inflammation while B2 receptor participates in the vasodilatory role of bradykinin5,6. Bradykinin analogs function is a similar fashion although depending on their structure they might have varying affinities to the receptors compared to bradykinin7. Also analogs of bradykinin have been synthesized that are specific to one of these receptors7.
Functions
Bradykinin is a potent endothelium-dependent vasodilator, causes contraction of non-vascular smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and also is involved in the mechanism of pain. Bradykinin also causes natriuresis, contributing to a drop in blood pressure8. Bradykinin raises internal calcium levels in neocortical astrocytes causing them to release glutamate9. Overactivation of bradykinin is thought to play a role in a rare disease called Hereditary Angioedema, also known as Hereditary Angio-Neurotic Edema10.
Some analogs of bradykinin have been found to have prolonged hypotensive action compared to bradykinin (Eg: beta-H-Pro-bradykinin)3. Some analogs have relative or even lower potencies compared to bradykinin (Eg: HArg1-Bradykinin and HArg9 Bradykinin)7. Other analogs have been studied for their potential of finding bradykinin antagonists that might be useful in the treatment of angio-neurotic edema.
References
1. Partridge, SM (1948). (Title or abstract not available), Biochem. J., 42, 238.
2. Allen PK, Kusumam J, Yoji S, Yoshitaka N, Berhane G, Sesha R and Michael S (1998). Bradykinin formation: Plasma and tissue pathways and cellular interactions. Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology, 16, 4, 403-429.
3. Ondetti MA, Engel SL (1975). Bradykinin analogs containing beta.-homoamino acid, J. Med. Chem.,18 (7), 761–763.
4. Roseli A, Gomes S, Jair RC, Luis J and Valdemar H (1996). Met-Lys-Bradykinin-Ser, the kinin released from human kininogen by human pepsin. Immunopharmacology, 32, 76-79.
5. Peter GM, Amrita A, and Mauro P (2000). Association between Kinin B1 Receptor Expression and Leukocyte Trafficking across Mouse Mesenteric Postcapillary Venules. J Exp. Med., 192, 367-380.
6. Duchene J, Lecomte F, Ahmed S, Cayla C, Pesquero J, Bader M, Perretti M and Ahluwalia A, (2007). A Novel Inflammatory Pathway Involved in Leukocyte Recruitment: Role for the Kinin B1 Receptor and the Chemokine CXCL5. J Immunol., 179, 4849-4856.
7. Max ES, Phyllis AL (1974). Synthesis and pharmacology of homoarginine bradykinin analog. J. Med. Chem., 17 (11), pp 1227–1228.
8. Dendorfer A, Wolfrum S, Wagemann M, Qadri F, Dominiak P, (2001). Pathways of bradykinin degradation in blood and plasma of normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol., 280:H2182
9. Kuoppala A, Lindstedt KA, Saarinen J, Kovanen PT, Kokkonen JO (2000). Inactivation of bradykinin by angiotensin-converting enzyme and by carboxypeptidase N in human plasma. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 278(4):H1069-74.
10. Bas M, Adams V, Suvorava T, Niehues T, Hoffmann TK, Kojda G (2007). Nonallergic angioedema: role of bradykinin. Allergy, 62(8):842-56.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.3892/or.2014.3366 | Bradykinin stimulates IL-6 production and cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.autneu.2015.07.006 | Afferent fibers involved in the bradykinin-induced cardiovascular reflexes from the ovary in rats | 下载 |
| 10.1159/000438526 | Exogenous Bradykinin Inhibits Tissue Factor Induction and Deep Vein Thrombosis via Activating the eNOS/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathway | 下载 |
| 10.1161/01.cir.95.5.1115 | Role of bradykinin in mediating vascular effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in humans | 下载 |
多肽H2N-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg-COOH的合成步骤:
1、合成CTC树脂:称取0.17g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.65mmol/g)和0.13mmol Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入0.33mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
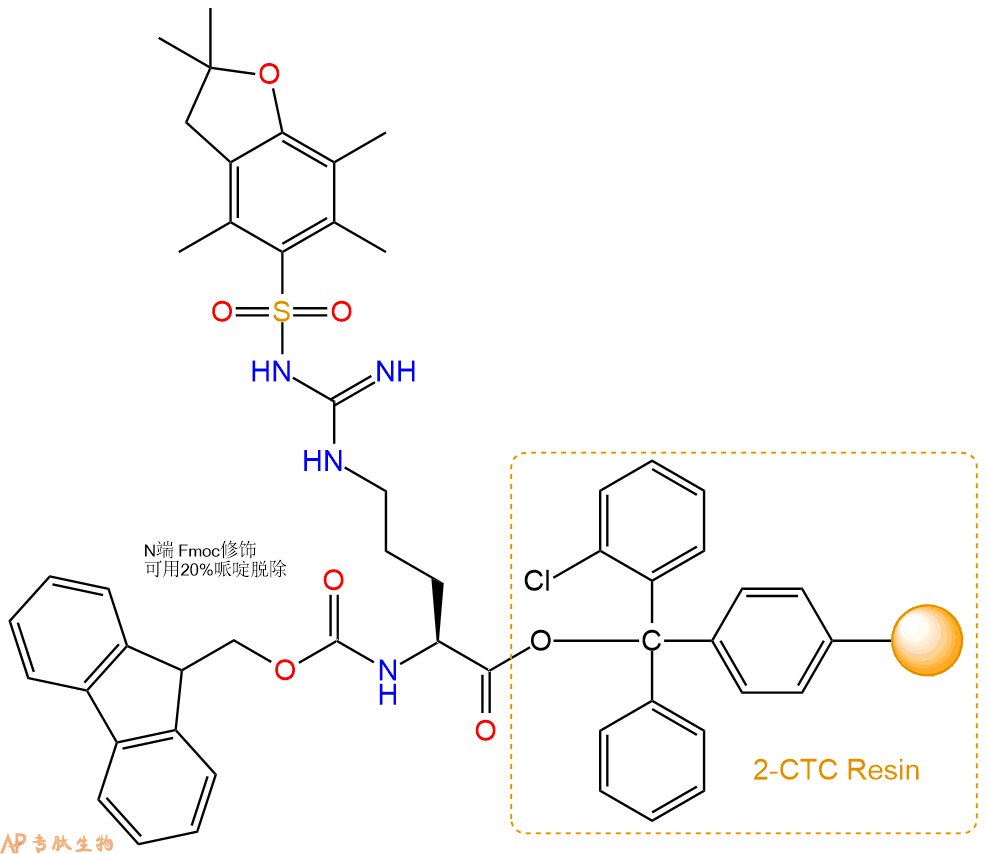
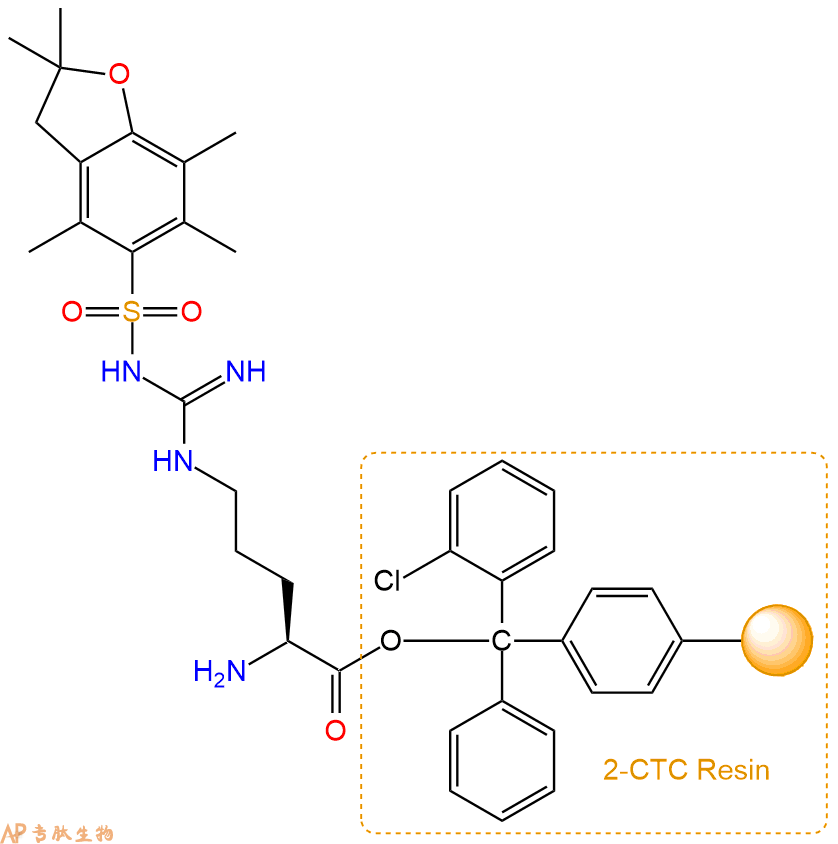
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
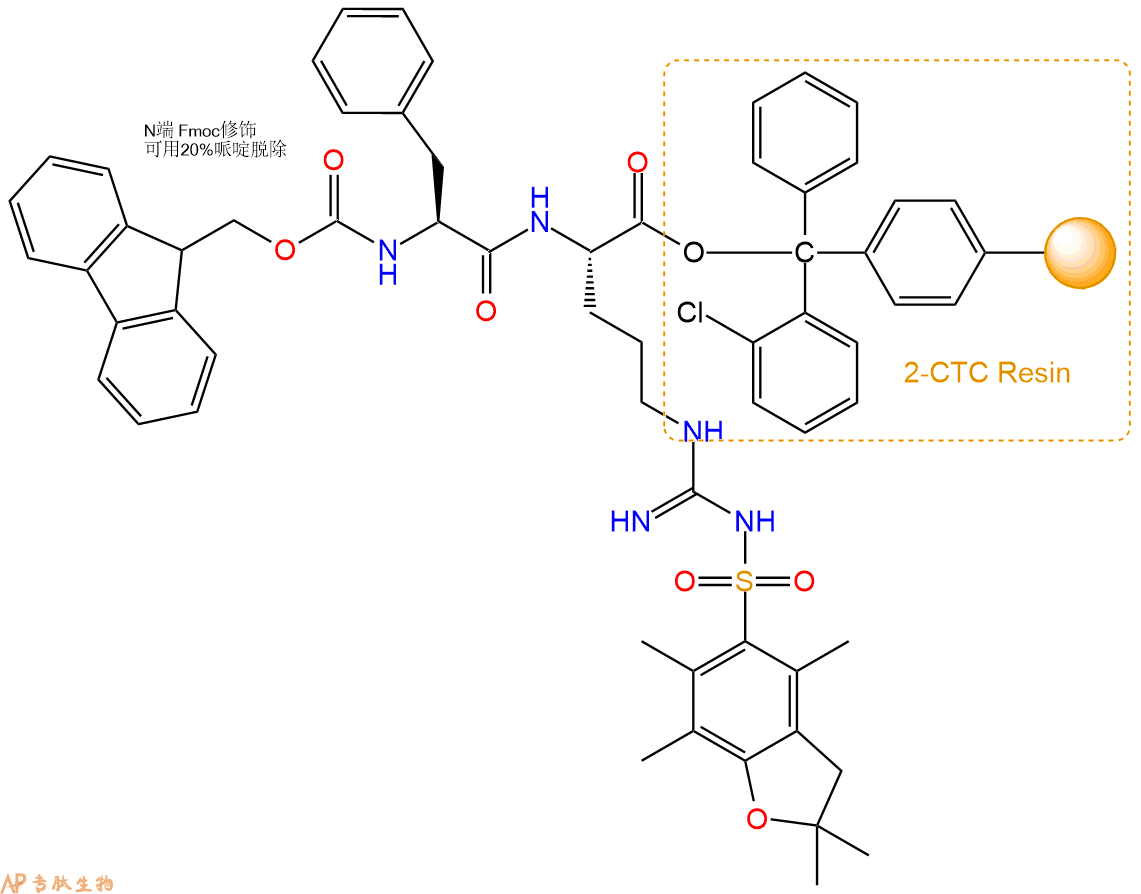
3、缩合:取0.33mmol Fmoc-Phe-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入0.66mmol DIPEA,0.31mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin,结构如下:

5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%、TFA:H2O=97.5%:2.5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。





